Handle Count Structure of Different Elasticsearch Versions #
To optimize performance in Elasticsearch 7.0 and later versions, search result matches are not accurately counted and the search result response body is adjusted. This will inevitably cause incompatibility with existing code. How can the problem be fixed quickly?
Structure Diff #
The search structure difference is as follows:
The search structure used by Elasticsearch before version 7.0 is as follows. total shows a specific value.
{
"took": 53,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 0,
"max_score": null,
"hits": []
}
}
The search structure used by Elasticsearch 7.0 and later versions is as follows. total shows a group of description scope objects.
{
"took": 3,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": {
"value": 10000,
"relation": "gte"
},
"max_score": 1,
"hits": []
}
}
Parameters Provided by Elasticsearch #
Elasticsearch 7.0 provides a parameter to accurately control the count. In other words, rest_total_hits_as_int=true can be added to the query request URL parameter so that the old structure is used. It is disabled by default.
Document URL: https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/search-search.html
However, you need to modify the program to add this parameter, and you may need to adjust the back-end code, front-end paging, and presentation. The modification workload may not be small.
Using INFINI Gateway for Quick Fixing #
If you do not want to modify the program, you can use INFINI Gateway to quickly repair the query and add query parameters to a search query.
In addition, INFINI Gateway can be used to limit the request sources for which query parameters are to be added. For example, request sources can be adjusted only for specific service calling parties. The following uses the curl command as an example to add query parameters only to queries from the curl debugging.
entry:
- name: es_entrypoint
enabled: true
router: default
network:
binding: 0.0.0.0:8000
router:
- name: default
default_flow: main_flow
flow:
- name: main_flow
filter:
- set_request_query_args:
args:
- rest_total_hits_as_int -> true
when:
and:
- contains:
_ctx.request.path: "_search"
- equals:
_ctx.request.header.User-Agent: "curl/7.54.0"
- record:
stdout: true
- elasticsearch:
elasticsearch: es-server
- dump:
response_body: true
elasticsearch:
- name: es-server
enabled: true
endpoints:
- http://192.168.3.188:9206
The final effect is as follows:
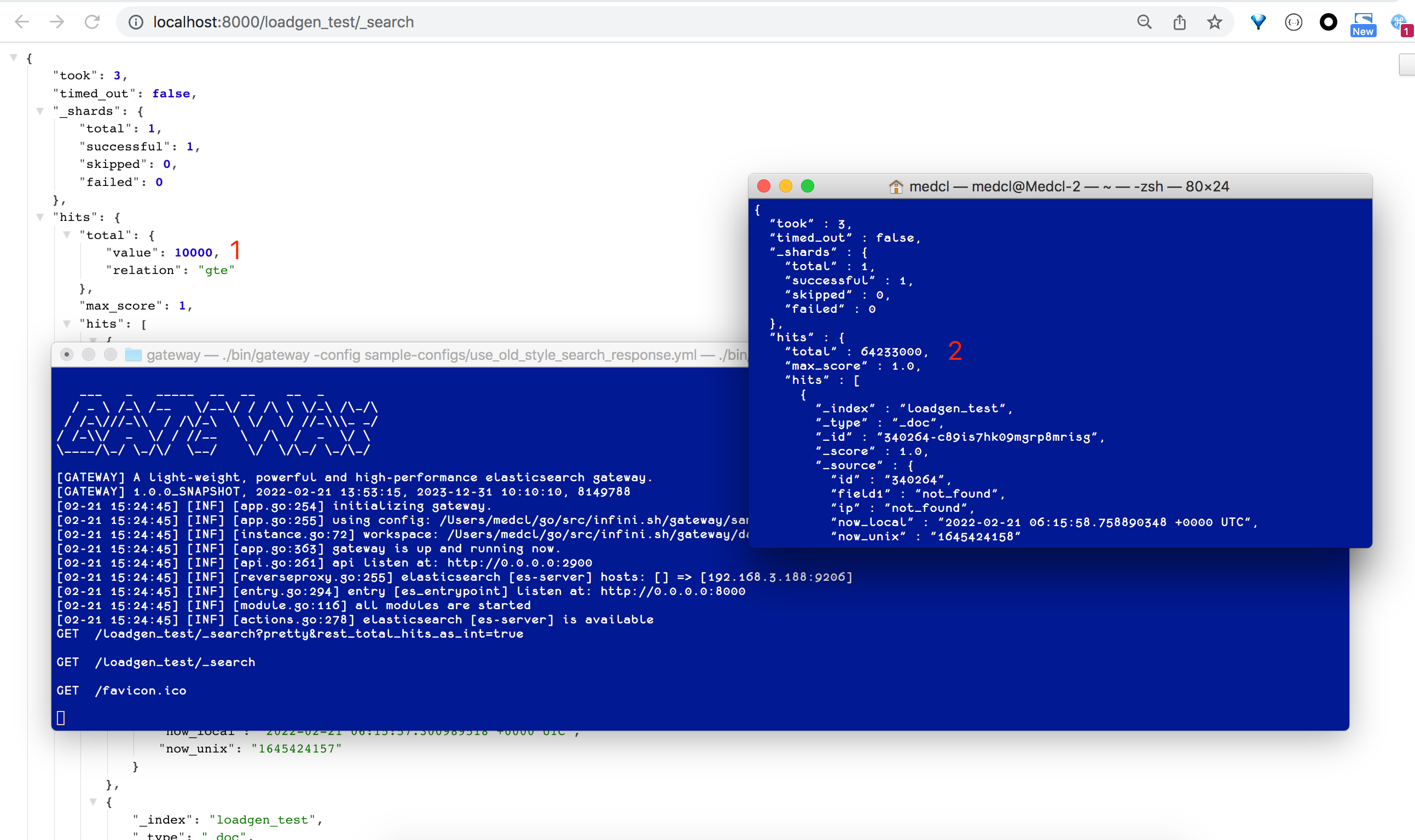
Figure 1 shows the search result returned after the gateway is accessed through a browser. Figure 2 shows the search result returned by the curl command. The User-Agent header information can match the curl command and only parameters are added to the search conditions to avoid affecting other requests.